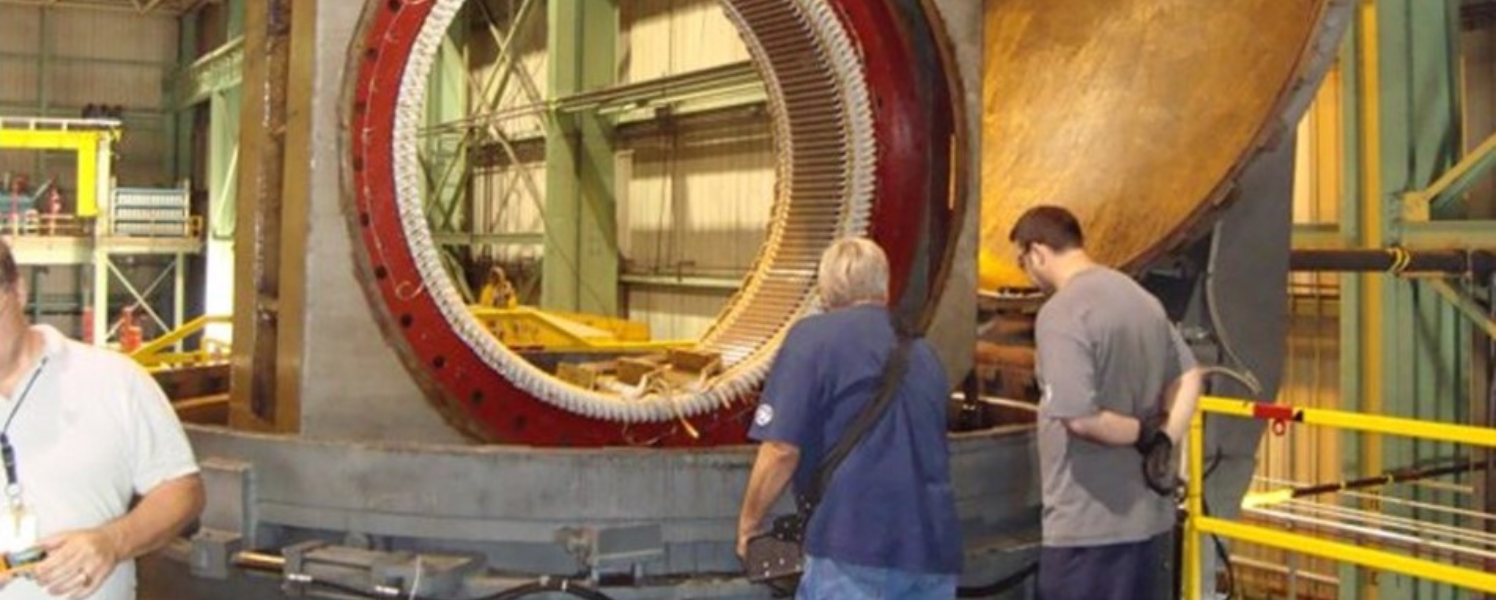
Vacuum Pressure Impregnation (VPI) is a method to insulate wound electro-mechanical parts thoroughly with a resin or varnish. VPI is a critical process to insulate and seal the porosity of the parts. VPI is essential to ensure that parts function correctly and improve the longevity of the equipment (Image 1). This blog is a guide that will explain the process, advantages and applications of VPI.
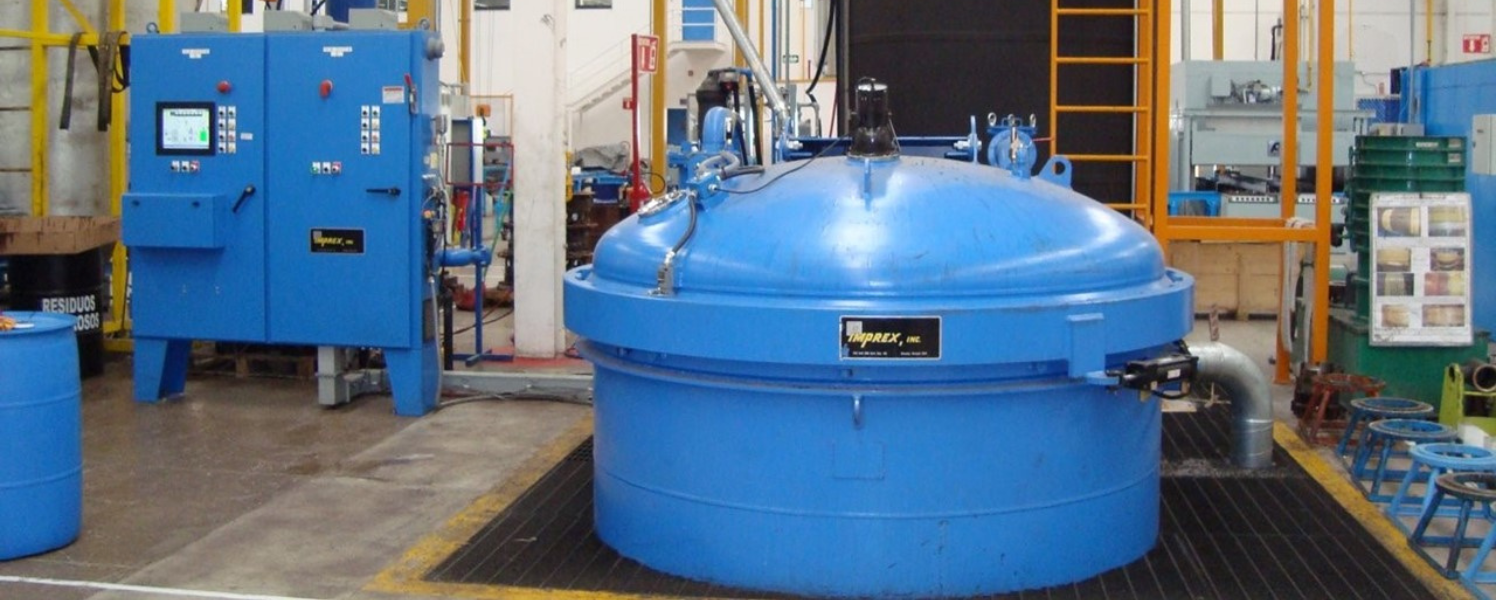

Image 1: Vacuum Pressure Impregnation (VPI) is an essential process to insulate wound electro-mechanical parts thoroughly with a resin or varnish.
VPI Process Explained
1. Pretreatment: The part is preheated in an oven.
2. Dry Vacuum Step: The part is placed in the pressure vessel, and the cover is closed. The vacuum is pulled to remove air or until a specified vacuum is achieved. This is the most critical step to ensure the part is fully encapsulated (Image 2).
3. Wet Vacuum Step: The transfer valve is opened, and the resin or varnish fills the impregnation chamber while under vacuum.
4. Pressure: The vacuum is released, and pressure is applied for the resin or varnish to penetrate the voids in the part entirely.
5. Release Pressure: Return unused resin or varnish to the holding tank.
6. Cure: The part is removed and placed in the customer’s oven for curing.
Image 2: The second step of the VPI process is when the part is placed in the pressure vessel, and the cover is closed.
The vacuum is pulled to remove air or until a specified vacuum is achieved. This is the most critical step to ensure the part is fully encapsulated.
Advantages of VPI
Without VPI, a component will deteriorate over time, leading to a failure in the product. This will increase costs and reduce quality. Here are the main advantages of using VPI.
1. Improve power output
A fully enclosed part leads to good heat transfer, keeping the electricity within the wires. This results in better part performance.
2. Contamination resistance
Contamination penetrates small openings in the unsealed insulation and produces a conducting path between turns or to-ground. Since VPI fully encloses the part, VPI ensures no risk of contamination.
3. Reduce coil vibration
The most common failure in motors is abrasion. Vibration causes wear and chaffing, leading to a part no longer being able to withstand voltage. Having a part enclosed with VPI serves as an adhesive between the motor strands as it turns. This reduces the risk of coil vibration.
VPI Applications
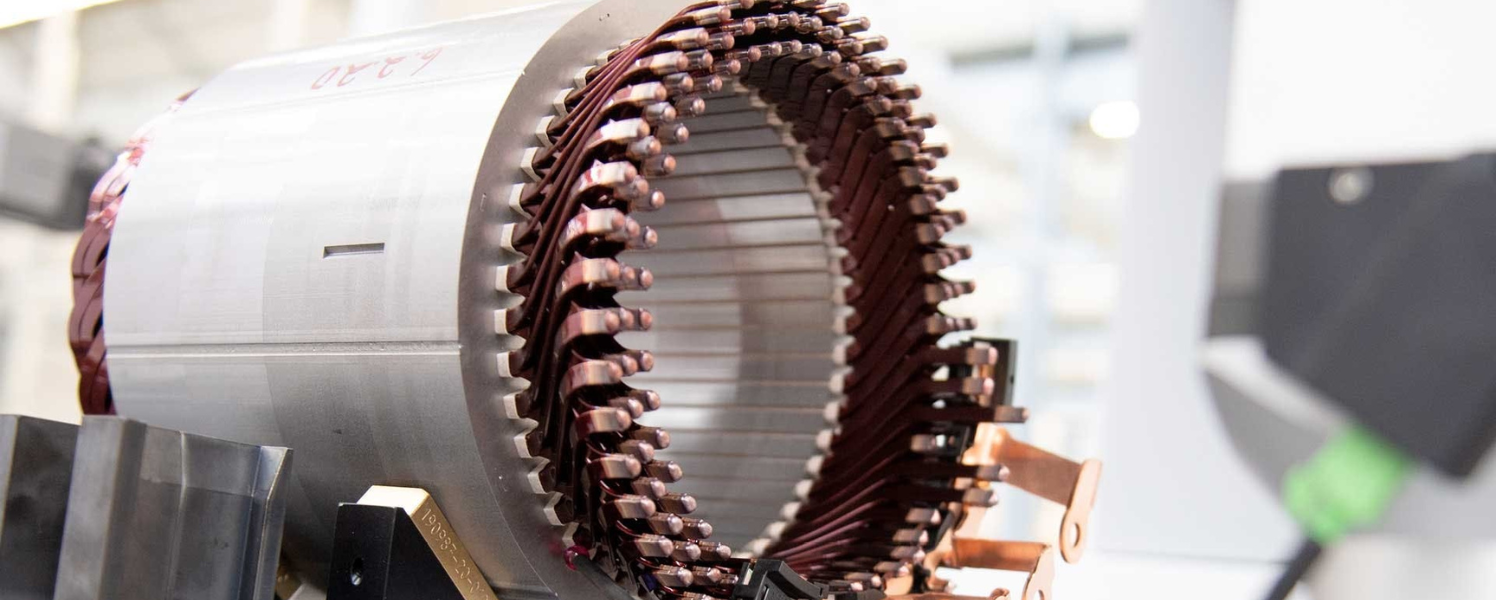
Typical applications of VPI are divided into two main categories (Image 3).
1. Electric Motors: Rotors, Stators
2. Electricity Delivery Equipment: Transformers, Capacitors, Super Capacitors
Image 3: Typical applications that use VPI include stators.
Image source: Electric Motor Engineering
In Summary
Vacuum Pressure Impregnation is the most efficient and effective way to enclose and insulate electro-mechanical parts. Using VPI ensures part performance while eliminating failure modes.